Subsidies
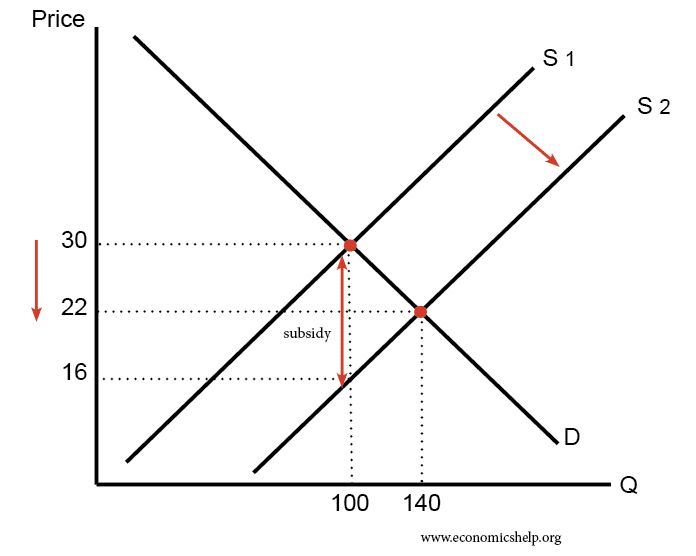
A subsidy is a grant (usually provided by the government) to encourage producers to increase the production of a good or service, resulting to a reduction in its price. The subsidy is usually paid directly to the producers, reducing their costs of production and therefore creating producer benefit. Some of this benefit is passed onto the consumer as the price of the good or service is lowered as the quantity produced increases. The supply curve shifts out because of the increase in production.
 |
| Subsidy |
Comments
Post a Comment