Normal profits, supernormal profits and losses
Profit maximisation
Occurs at:
MC = MR
where MC cuts MR from below (as where it cuts from above is point of profit minimisation)
This is because past this point MR < MC, and each additional good is costing the firm more than it is making. Before that point MR > MC so the firm can increase profit by producing more.
NB - point of prof max can be found using TC and TR:
Normal and supernormal profit and losses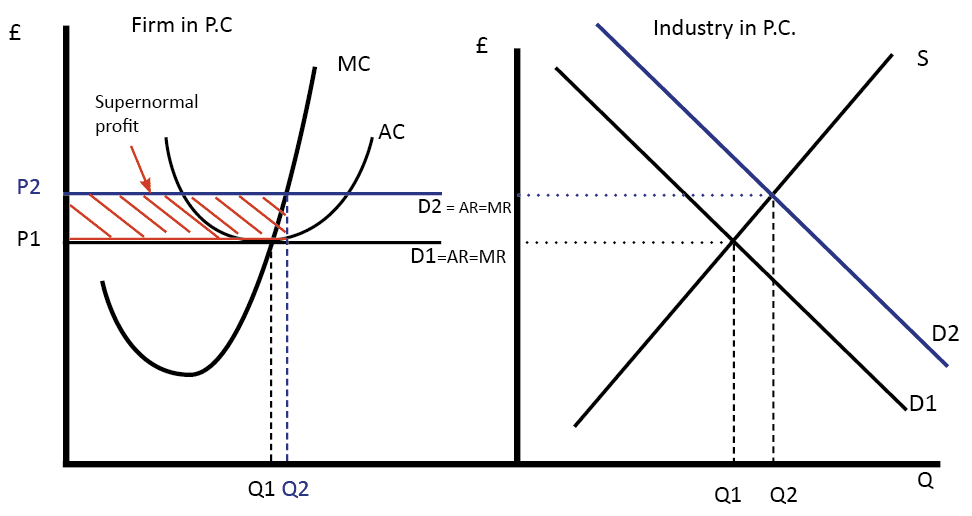
Normal profit is profit that covers the opportunity cost of capital and is just sufficient to keep the firm in the market.
Supernormal/economic profit are profits that exceed normal profits.
When AC lies below AR at the point of output, the difference between AR and AC is the supernormal profit on that unit output. The overall supernormal profit is the difference times the quantity sold (Q2 in the above).
Likewise, when AC lies above AR at the point of output, the company makes supernormal losses.
SR and LR shut-down prices: diagrammatic analysis
The SR shut-down condition is where
AR < AVC
because fixed costs are sunk costs, and were a firm to shut down it would not be able to recover these costs. So as long as it can cover its variable costs in the SR, it can pay off FC later on rather than shutting down and being unable to recover them.

The LR shut-down condition is where:
AR < LRAC
as in the LR all FoPs are variable.
Comments
Post a Comment